Write Prolog clauses expressing the following facts:
Write Prolog queries asking the following questions:
Write a single clause that is equivalent to all the of the following facts:
parent(charles, wenceslaus). parent(charles, margaret). parent(charles, sigismund).
Write a single clause that is equivalent to all the of the following facts:
parent(charles, wenceslaus). parent(charles, margaret). parent(charles, sigismund). parent(sigismind, elizabeth).
Consider this Prolog program:
male(hans). male(charles). female(elizabeth). female(kate). dance(P, Q) :- male(P), female(Q).
What answers will these queries produce, and in what order?
dance(charles,
X).dance(jacob, radka).dance(kate, X).dance(X, elizabeth).dance(X, X).dance(hans, elizabeth).dance(X, john).dance(X, Y).Consider this Prolog program:
drinks(thomas, whiskey). drinks(sonya, beer). drinks(lucy, wine). drinks(radek, beer). drinks(jarda, beer). pair(P, Q, D) :- drinks(P, D), drinks(Q, D).
What answers will these queries produce, and in what order?
pair(P,
thomas, whiskey).pair(sonya, jarda, beer).pair(thomas, sonya, beer).pair(radek, radek, beer).pair(X, Y, beer).pair(X, Y, Z).Consider this predicate:
foo(a). foo(b). foo(X) :- foo(X).
Consider the following queries. What answer(s) will they produce? Will they terminate?
foo(Y).
foo(Y), true.
foo(Y), false.
true, foo(Y).
false, foo(Y).
Suppose that we move the rule to the
top:
foo(X) :- foo(X).
foo(a).
foo(b).
Now
what answer(s) will be produced by the query 'foo(Y)'?
Consider this acyclic directed graph:
We can write a Prolog predicate representing adjacency between vertices:
edge(a, b). edge(a, e). edge(b, c). edge(b, f). edge(e, d). edge(e, f). edge(f, c). edge(g, d). edge(g, h). edge(h, f).
Write a predicate path(V, W)
that is true if there is some path from V to W in the directed
graph.
Given your predicate, what answers will each of these queries produce?
path(f,
f).path(a, c).path(g, e).path(g, X).path(X, h).path(X, X).path(X, Y).Suppose that we define a family tree using
predicates male, female and parent:
male(john). male(charles). male(wenceslaus). female(anne). female(elizabeth). parent(wenceslaus, anne). parent(wenceslaus, charles). parent(charles, john). parent(charles, elizabeth). ...
Write Prolog predicates expressing the following relationships:
grandmother(G, X)
sibling(X, Y)
Two people are siblings if they have at least one parent in common.
full_sibling(X, Y)
Full siblings share both parents.
first_cousin(X,
Y), second_cousin(X, Y)
First cousins have parents who are full siblings. Second cousins have parents who are first cousins.
cousin(X,
Y)
Two people are cousins if they are Nth cousins for any N ≥ 1.
Consider a map that shows 7 countries in central Europe:
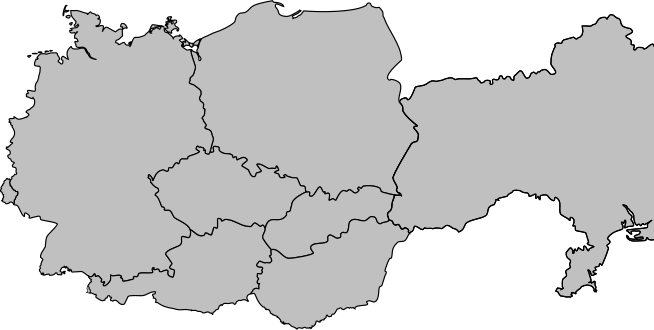
Is it possible to color this map with 3 colors so that no bordering countries have the same color?
Write a Prolog program that can answer this question.
Suppose that we'd like to fill in a 3 x 3 grid with letters so that every row and column contains one of these words:
AGE, AGO, CAN, CAR, NEW, RAN, ROW, WON
Write a Prolog program that can find all possible solutions.
Consider the following tiny Minesweeper board of dimensions 5 x 2:

A number N means that there are N mines in adjacent squares (which may be adjacent horizontally or diagonally).
Write a Prolog program that can find all possible positions for the mines.
Write a Prolog program that can solve the following puzzle.
Kate, Maria and Roman have distinct occupations and play distinct musical instruments. Their occupations are doctor, lawyer, and teacher, and the instruments they play are piano, flute, and violin. Also:
Maria lives next to the doctor.
The lawyer plays the piano.
Maria is not the teacher.
Kate is a patient of the violinist.
Who plays the flute?